Benefits of learning Persian (Farsi)
Learning Persian (Farsi) offers numerous benefits, including enhanced communication with over 100 million Persian speakers, expanded professional opportunities in fields like business and diplomacy, a deeper understanding of Persian culture and heritage, improved travel experiences in Iran and neighboring countries, access to academic and research resources, cognitive benefits, personal growth, easier language learning for Arabic or Urdu speakers, access to a rich literary tradition, and the potential for cultural diplomacy and fostering cross-cultural understanding.

Here are some key advantages of learning Persian:
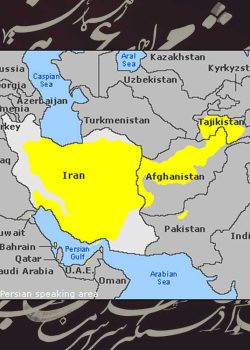
- Communication: Persian is spoken by over 100 million people worldwide, primarily in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and parts of Central Asia. By learning Persian, you gain the ability to communicate with native speakers in these regions, opening up new opportunities for travel, business, and cultural exchange.
- Professional Opportunities: Persian is an important language for business, diplomacy, and international relations, particularly in the Middle East and Central Asia. Proficiency in Persian can enhance your career prospects, especially if you’re interested in fields such as international relations, translation, journalism, academia, or working for NGOs.
- Cultural Understanding: Persian has a rich history and is closely tied to the cultural heritage of Iran, one of the oldest civilizations in the world. By learning Persian, you gain access to a vast array of literature, poetry, art, music, and films, deepening your understanding of Persian culture and fostering cross-cultural appreciation.
- Travel and Tourism: Iran is a country of immense beauty, with stunning landscapes, historical sites, and vibrant cities. Learning Persian allows you to navigate the country more comfortably, interact with locals, and gain a deeper understanding of its culture, traditions, and history.
- Academic and Research Opportunities: Persian is a significant language for academic research, especially in fields such as history, archaeology, linguistics, literature, religious studies, and political science. Learning Persian can provide you with access to a wealth of primary sources and enable you to engage with Persian scholarship.
- Cognitive Benefits: Learning Persian can enhance your cognitive abilities. Studies have shown that learning a new language improves memory, problem-solving skills, and overall brain function. It can also increase your ability to think flexibly and creatively.
- Personal Growth: Learning any language, including Persian, broadens your horizons and promotes personal growth. It challenges you to think differently, understand diverse perspectives, and develop empathy. It can also boost your self-confidence as you make progress in acquiring a new skill.
- Opportunities for Language Learning: Persian shares some similarities with other Indo-European languages, such as Arabic and Urdu. If you already know one of these languages, learning Persian becomes easier due to shared vocabulary and grammatical structures. Additionally, learning Persian can serve as a stepping stone to learning other Central Asian languages.
- Access to Persian Literature: Persian literature is renowned worldwide for its beauty and depth. From ancient poets like Rumi, Hafez, and Ferdowsi to modern writers like Sadegh Hedayat and Simin Daneshvar, Persian literature offers a treasure trove of poetic and philosophical works. Learning Persian allows you to read these masterpieces in their original language and appreciate the nuances of their meaning.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Given the geopolitical importance of Iran and its relations with other countries, learning Persian can facilitate cultural exchange and bridge gaps between different cultures. It enables you to engage in dialogue, understand different perspectives,
and promote cross-cultural understanding.
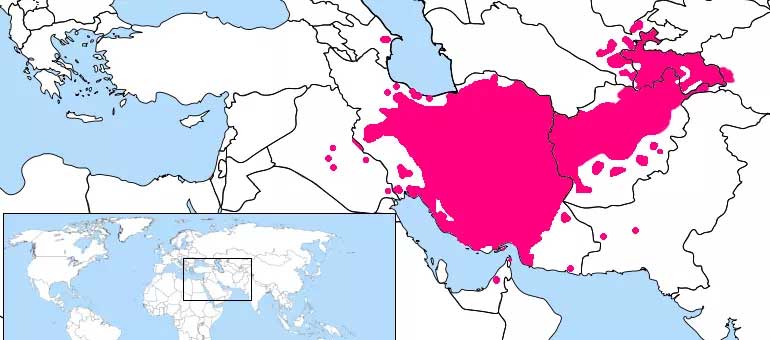
Persian Language History
The Persian language, known as Farsi, boasts a remarkable history spanning over two millennia. Its origins can be traced back to Old Persian, spoken during the Achaemenid Empire, followed by the emergence of Middle Persian during the Sasanian Empire. However, it was during the Islamic Golden Age that Persian experienced a flourishing period as a literary language, known as Classical Persian. This era saw the production of masterpieces by renowned poets such as Ferdowsi, Rumi, Saadi, and Hafez, who contributed to its rich poetic tradition.
Despite the dominance of Arabic as the language of administration and religion, Persian continued to thrive as a spoken and literary language. Over time, it underwent transformations influenced by Arabic and absorbed numerous loanwords. In the 19th century, Persian underwent a process of modernization, simplification, and standardization, leading to the development of Modern Persian (Farsi) as the official language of Iran. Today, Persian stands as a testament to the literary, cultural, and intellectual heritage of the Persian-speaking world, with its poetic, philosophical, and scientific contributions making it a language of immense cultural significance.
Is Persian Hard to Learn?
The difficulty of learning Persian (Farsi) varies depending on individual factors, but it can be considered moderately challenging for English speakers. While Persian uses a different alphabet and has unique sounds, its pronunciation is generally phonetic. Grammar can be manageable with regular patterns, although verb conjugation and noun declension require memorization. Vocabulary presents a mix of Arabic loanwords and shared Indo-European roots. Overall, while Persian may require some effort and dedication, with consistent practice and access to quality resources, it is an attainable language to learn.
Here are some considerations regarding the difficulty of learning Persian:
- Alphabet: Persian uses the Arabic script with some additional letters, making it necessary to learn a new writing system if you are unfamiliar with Arabic or related scripts. This can pose an initial challenge, but with practice and guidance, it can become manageable.
- Pronunciation: Persian pronunciation is generally phonetic, meaning that words are pronounced as they are spelled. However, there are some unique sounds in Persian, such as the “kh” (خ) sound, which may take time to master. With practice and exposure to native speakers, you can improve your pronunciation.
- Grammar: Persian has a relatively regular and straightforward grammar compared to some other languages. It follows subject-object-verb (SOV) word order and has grammatical features such as noun-adjective agreement and case markers. While some aspects of Persian grammar, like verb conjugation and noun declension, require memorization, they follow predictable patterns.
- Vocabulary: Persian has a significant number of loanwords from Arabic, which can be challenging if you are not familiar with the Arabic language. However, Persian also shares vocabulary with other Indo-European languages, such as English, French, and Spanish, due to its historical connections. This can facilitate learning for speakers of these languages.
- Dialects: Persian has regional dialects, such as Dari in Afghanistan and Tajik in Tajikistan, which have some linguistic variations. While the standard Persian (Farsi) is understood throughout the Persian-speaking world, exposure to different dialects might require some adjustment.
- Language Proficiency Goals: The difficulty of learning Persian also depends on your language proficiency goals. Basic conversational skills can be acquired relatively quickly, but achieving higher levels of fluency and proficiency may require more time and effort.
However, the moment you begin to study the alphabet, you will find many similarities with European languages. That’s because the Persian language is also an Indo-European language, meaning that it shares the same origin as most European languages, making Persian grammar relatively easy to learn and understand.
- Bad (English) = Bad (Persian)
- Star (English) = Setareh (Persian)
- Mother (English) = Madar (Persian)
- Padre (Spanish) = Pedar (Persian)
- Tochter (German) = Dokhtar (Persian) = Daughter (English)
- Name (English) = Naam (Persian) = Naam (Dutch)

Best Farsi Learning Resource!
When it comes to learning Persian (Farsi), there are several excellent resources available. Here are some of the best resources for learning Farsi:
- “Persian Language Online” (https://www.persianlanguageonline.com): This comprehensive online course, developed by the University of Texas at Austin, offers interactive lessons, exercises, audio recordings, and cultural insights. It covers various proficiency levels and provides a solid foundation in Persian grammar, vocabulary, and conversational skills.
- “Chai and Conversation” (https://www.chaiandconversation.com): This podcast-based learning resource is designed to teach conversational Persian. It provides engaging and practical lessons that cover useful phrases, grammar, and cultural aspects. The podcast is accompanied by PDF guides, vocabulary lists, and exercises.
- “Easy Persian” (https://www.easypersian.com): This website offers a comprehensive collection of lessons, grammar explanations, vocabulary lists, and exercises for learners of all levels. It covers both colloquial and formal Persian, making it suitable for different language goals.
- “PersianPod101” (https://www.persianpod101.com): This popular podcast and online learning platform provide audio and video lessons, vocabulary lists, grammar explanations, and cultural insights. It offers a structured curriculum and a wide range of resources for learners at various proficiency levels.
- “Transparent Language” (https://www.transparent.com): Transparent Language offers a Persian course that combines interactive lessons, vocabulary, grammar explanations, and cultural notes. The platform allows learners to practice their listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills through a variety of exercises and activities.
- “Colloquial Persian” by Abdi Rafiee: This textbook is part of the “Colloquial Series” and offers a practical approach to learning Persian. It includes dialogues, exercises, grammar explanations, and cultural information, making it suitable for self-study or classroom use.
- “Living Language Farsi” (https://www.livinglanguage.com): This comprehensive coursebook, audio program, and online resources provide a well-rounded approach to learning Persian. It covers essential vocabulary, grammar, and conversational skills, with interactive exercises and cultural insights.
- Language exchange platforms: Websites and apps like iTalki (https://www.italki.com) and Tandem (https://www.tandem.net) connect language learners with native Persian speakers for language exchange sessions or private tutoring. These platforms offer opportunities to practice speaking and receive personalized guidance.
In conclusion
Learning Persian (Farsi) offers a wealth of benefits. It provides opportunities for effective communication with millions of speakers, enhances professional prospects in various fields, fosters cultural understanding and appreciation, facilitates travel and tourism experiences, opens doors to academic and research opportunities, and promotes cognitive growth and personal development. Additionally, delving into Persian literature, poetry, and cultural traditions enriches one’s understanding of this ancient language and its contributions to human history. Whether for practical, academic, or personal reasons, embarking on the journey of learning Persian can be a rewarding endeavor that broadens horizons, deepens connections, and expands one’s perspective of the world.
Related Posts