Learn Persian alphabet
Learning a new alphabet can be an exciting and rewarding experience. Whether you’re delving into a new language or exploring a different culture, mastering a new alphabet opens up a world of possibilities. However, it can also seem daunting at first, especially if you’re accustomed to a different writing system. With the right approach and resources, you can embark on this linguistic adventure with confidence.
Why do we need to learn a new alphabet?
Learning a new alphabet offers several important benefits and reasons why it can be beneficial:
Language Acquisition: Many languages around the world use different writing systems and alphabets. By learning a new alphabet, you gain the ability to read, write, and understand languages that use that particular script. This opens up opportunities for language acquisition and allows you to engage with a wider range of cultures and communities.
Cultural Understanding: Alphabets are closely tied to the cultures and histories of the languages they represent. By learning a new alphabet, you gain insight into the cultural nuances, traditions, and identities of the people who use that writing system. It enhances your understanding and appreciation of different cultures, fostering intercultural competence and empathy.
Communication and Connection: Learning a new alphabet facilitates communication with speakers of languages that use that script. It enables you to read and write messages, emails, documents, or social media posts in the language, improving your ability to connect with individuals from different backgrounds. It can enhance travel experiences and build meaningful relationships with people from diverse linguistic communities.
Personal and Cognitive Development: Learning a new alphabet challenges your brain and enhances cognitive abilities. It stimulates memory, attention, and problem-solving skills as you navigate and internalize the new characters and their corresponding sounds. It promotes personal growth, perseverance, and a sense of accomplishment as you overcome the challenges associated with learning a new system of writing.
Educational and Professional Opportunities: Knowledge of a new alphabet can be advantageous in educational and professional settings. It expands your language skills, making you a more competitive candidate for language-related positions or academic pursuits. It can also be useful in research, translation, cultural studies, and international business contexts.
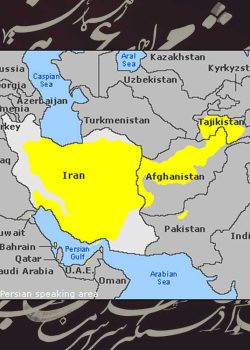
Persian alphabet:
The Persian alphabet is known as the Perso-Arabic script. It is an Arabic-based script with a few additional letters to accommodate sounds specific to the Persian language. The Persian alphabet consists of 32 letters, and it is written from right to left. Here’s a guide to the Persian alphabet, including the letter name, transliteration, and pronunciation:

It is an adaptation of the Arabic script with a few additional letters to accommodate sounds specific to the Persian language.
Here are some key features of the Persian script:
- Right-to-Left Direction: Like the Arabic script, the Persian script is written from right to left. This means that the text progresses from the right side of the page to the left side, and the lines are arranged vertically from top to bottom.
- Arabic Script Adaptation: The Persian script is derived from the Arabic script but has some modifications to represent sounds specific to Persian. It retains the basic letter shapes and most of the letter names from Arabic.
- Ligatures: Ligatures are common in the Persian script. A ligature is a combination of two or more letters joined together. Ligatures are used to connect letters smoothly, especially in cursive handwriting. Ligatures also help maintain consistent spacing between letters.
- Diacritical Marks: Diacritical marks, called “Harakat” in Arabic, are used in the Persian script to indicate short vowels. They are small symbols placed above or below the letters to represent vowel sounds. In practice, however, diacritical marks are not frequently used in written Persian except in specific contexts like teaching materials or religious texts.
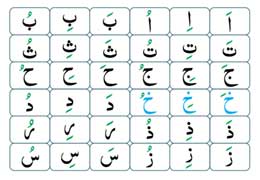
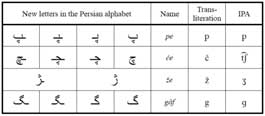
Additional Letters: The Persian script has several additional letters compared to the standard Arabic script. These additional letters represent sounds that are specific to the Persian language but not found in Arabic. Some examples include “پ” (pe), “چ” (che), and “ژ” (zhe) “گ” (g).
Calligraphic Tradition: Persian calligraphy is highly esteemed as an art form, with a long history and various styles. Calligraphy plays a significant role in Persian culture, and skilled calligraphers are admired for their ability to create beautiful and intricate scripts.

The Persian language, also known as Farsi, has several notable features that contribute to its unique characteristics. Here are some key features of the Persian language:
Poetry and Literature: Persian has a long tradition of poetry and literature. Classical Persian poetry, particularly from the medieval period, is highly esteemed and includes works by renowned poets such as Rumi, Hafez, and Saadi. Persian literature covers a wide range of genres, including epic poetry, mystic poetry, and prose.
VSO Word Order: Persian follows a verb-subject-object (VSO) word order, which means that the verb typically appears before the subject and object in a sentence. For example, “I see the book” would be expressed as “Mān ketāb-rā mibīn-am” (literally, “See-I book-the”). من کتاب را میبینم
Noun Declensions: Persian nouns are not inflected for case, but they can be marked for definiteness (with the suffix “-e”) and plurality (with the suffix “-hā”). Adjectives generally agree with the noun they modify in terms of number and definiteness.
Pronouns and Honorifics: Persian has a complex system of pronouns that distinguishes between formal and informal forms, as well as different levels of politeness and familiarity. Honorific titles, such as “khanom” for Mrs./Ms. and “aghā” for Mr., are commonly used to address individuals respectfully.
Vowel System: Persian has a relatively simple vowel system consisting of short and long vowels. The short vowels include /a/, /e/, /o/, while the long vowels include /ā/, /i:/, /u:/.
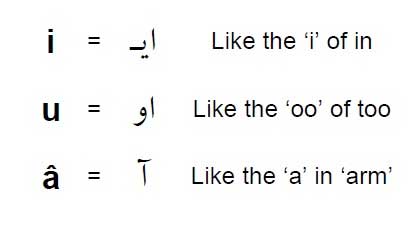
Loanwords: Persian has borrowed vocabulary from various languages throughout its history. Arabic, French, and English are among the languages that have contributed loanwords to Persian, particularly in scientific, technical, and modern domains.
The history of the Persian alphabet is closely intertwined with the development and evolution of the Persian language itself. The Persian alphabet has undergone several transformations throughout history and it reflects the dynamic interaction between linguistic, cultural, and historical factors.
Read More:
5 Best Persian Podcasts for Farsi Learners
Related Posts