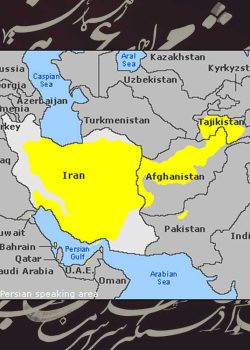
Persian, also known as Farsi, is a language spoken by over 100 million people worldwide. It is the official language of Iran and is also widely spoken in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and other countries. Persian is an Indo-European language written in the Persian script, a modified version of the Arabic script, and will explore the Persian language’s history, grammar, vocabulary, and cultural significance.
History of the Persian Language
The Persian language has a long and rich history of over 2,500 years. The earliest records of
Persian are found in inscriptions from the Achaemenid Empire, which ruled over Iran from 550 BCE to 330 BCE. During this period, Old Persian was the empire’s official language, and it was used for administrative purposes and official correspondence.
After the fall of the Achaemenid Empire, Middle Persian (also known as Pahlavi) became the dominant language in Iran and was heavily influenced by Semitic languages such as Aramaic and significantly impacted the development of modern Persian.
The modern Persian language emerged during the Safavid dynasty in the 16th century. The Safavids made Persian the official language of the court and promoted it as the language of culture and literature. As a result, Persian became the dominant language in Iran and a symbol of Iranian identity.
The Iranian language family can be divided into two main groups: Western Iranian languages and Eastern Iranian languages.
Western Iranian languages are spoken in Iran and include Persian (Farsi), Kurdish, Baluchi, and Luri. Persian (Farsi) is the most widely spoken language in Iran and is the official language of the country, and is spoken mainly in the western part of Iran, in Iraq, Turkey, and Syria, in the southeastern part of Iran, as well as in Pakistan and Afghanistan, and in the central and southwestern parts of Iran.
Eastern Iranian languages, including Pashto, Tajik, and other minor languages, are spoken in Afghanistan and Central Asia. Pashto is the official language of Afghanistan and is also spoken in parts of Pakistan. Tajik is spoken in Tajikistan and parts of Uzbekistan and is a variety of Persian. Other Eastern Iranian languages include Wakhi, Munji, and Yidgha.
Several languages and dialects have evolved within each group due to various historical, social, and cultural factors. These languages and dialects have unique features and characteristics, such as pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar differences.
Overall, the Iranian language family is a diverse and complex group of languages that reflects the region’s rich linguistic and cultural heritage.

Grammar of Persian Language
Persian is an inflected language, meaning a word’s meaning can change depending on its suffixes and prefixes. For example, the Persian language has six grammatical cases: nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and locative. The verb comes at the end of a sentence in Persian, and the tense is indicated by prefixes or suffixes.
The Persian language has a complex system of honorifics used to show respect or politeness to the person being addressed. Persian has three levels of honorifics: formal, informal, and intimate. The use of honorifics is an essential aspect of Persian culture and is considered a sign of good manners and respect.
The vocabulary of the Persian Language
The Persian language has a rich vocabulary that includes words from the region’s Arabic, Turkish, and other languages. Persian has many loanwords from Arabic, which reflect the influence of Islam on the tongue. Persian also has loanwords from Turkish, which reflect the impact of the Ottoman Empire on the region.
The Persian language has a unique system of word formation, which allows for creating new words by adding prefixes and suffixes to existing terms. This system is particularly useful in poetry and literature, where writers can create new comments to fit their needs.
Cultural Significance of the Persian Language
The Persian language has played an essential role in the culture and history of Iran and the wider region. Persian literature is one of the richest and most diverse in the world, with works ranging from epic poetry to modern novels. The Persian language has also been instrumental in the spread of Islam, as many of the early Islamic scholars and philosophers wrote in Persian. Persian has also significantly impacted the development of other languages in the region. Urdu, for example, is a language that developed from a mixture of Persian and Hindi and is widely spoken in Pakistan and India.
Conclusion
Persian (Farsi) language has a rich and diverse range of dialects that reflect the cultural and linguistic diversity of the Persian-speaking world. The Persian language has been spoken in the region for over two and a half millennia, and over time, different dialects have emerged, each with its unique vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation.
Regional dialects in Persian are often shaped by the geography, history, and cultural traditions of the area where they are spoken. Persian dialects can be broadly divided into two categories: Western Persian dialects and Eastern Persian dialects. The Western Persian dialects are spoken in Iran, while the Eastern Persian dialects are spoken in Afghanistan and Tajikistan.
Western Persian Dialects
- Tehrani Dialect: The Tehrani dialect is spoken in the capital city of Tehran and is considered the standard Persian dialect. It is widely used in the media, education, and government. The Tehrani dialect has a distinctive accent and vocabulary, with pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary differences from other dialects.
- Esfahani Dialect: The Esfahani dialect is spoken in Isfahan and is known for its slow and melodic intonation. It has a unique vocabulary and grammar, with differences in pronunciation and language from other dialects.
- Shirazi Dialect: The Shirazi dialect is spoken in Shiraz and is known for its poetic and musical quality. It has a distinctive accent and vocabulary, with pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary differences from other dialects.
- Kashani Dialect: The Kashani dialect is spoken in Kashan and has a distinct accent and vocabulary. It is influenced by the neighboring dialects of Esfahani and Tehrani.
- Kermani Dialect: The Kermani dialect is spoken in the province of Kerman and has a unique vocabulary and grammar. It is influenced by the neighboring dialects of Shirazi and Tehrani.
Eastern Persian Dialects
- Herati Dialect: The Herati dialect is spoken in the city of Herat in Afghanistan and has a distinct accent and vocabulary. It is influenced by the neighboring dialects of Dari and Pashto.
- Kabuli Dialect: The Kabuli dialect is spoken in the city of Kabul in Afghanistan and is the most widely spoken dialect in the country. It has a distinctive accent and vocabulary, with differences in pronunciation, grammar, and language from other dialects.
- Tajiki Dialect: The Tajiki dialect is spoken in Tajikistan and has a unique vocabulary and grammar. It is heavily influenced by the Russian language and differs in pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary from other dialects.
- Dari Dialect: The Dari dialect is spoken in Afghanistan and is heavily influenced by the Persian spoken in Iran. It has a unique vocabulary and grammar, with pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary differences from other dialects.
- Hazaragi Dialect: The Hazaragi dialect is spoken by the Hazara people in Afghanistan and has a unique vocabulary and grammar. It is influenced by the neighboring dialects of Dari and Pashto.

Differences Between Persian Dialects
Persian dialects differ in several ways, including pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. For example, the Tehrani dialect is known for its distinct accent and language, while the Esfahani dialect is known for its slow and melodic intonation. The Shirazi dialect is known for its poetic and musical quality, while the Kabuli dialect is Afghanistan’s most widely spoken dialect. Some dialects have unique vocabulary and grammar, while others are influenced by neighboring dialects or languages. For example
In conclusion, the Persian language is a complex and fascinating language that has played an essential role in the history and culture of Iran and the wider region. Its rich vocabulary, complicated grammar, and unique system of word formation make it a language that is both challenging and rewarding to learn. The Persian language is a testament to the diversity and richness of the human experience and continues to be an essential language.
Persian (Farsi) language is a member of the Iranian branch of the Indo-European language family and has several unique characteristics that distinguish it from other languages.
- Script: Persian is written in the Persian script, a modified version of the Arabic script. It is written from right to left and contains 32 letters.
- Grammar: Persian is an inflected language, meaning a word’s meaning can change depending on its suffixes and prefixes. Persian has six grammatical cases: nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and locative.
- Vocabulary: Persian has a rich vocabulary that includes words from the region’s Arabic, Turkish, and other languages. Persian has many loanwords from Arabic, reflecting Islam’s influence on the language.
- Honorifics: Persian has a complex system of honorifics used to show respect or politeness to the person being addressed. Persian has three levels of honorifics: formal, informal, and intimate.
- Poetry: Persian is a language of poetry and literature with a long tradition of poetic expression. Persian poetry is known for its beauty, depth, and complexity, and it has had a significant impact on language development.
- Regional Dialects: Persian has several regional dialects, which vary in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. The most widely spoken dialect is Tehrani, which is spoken in the capital city of Tehran.
Overall, the Persian language is complex and fascinating, reflecting the rich linguistic and cultural heritage of the Persian-speaking world. Its unique characteristics have made it an essential language in literature, culture, and diplomacy, and it continues to be a vital part of the Iranian and Persian-speaking communities.
Read More:
Benefits of learning Persian (Farsi)
Related Posts